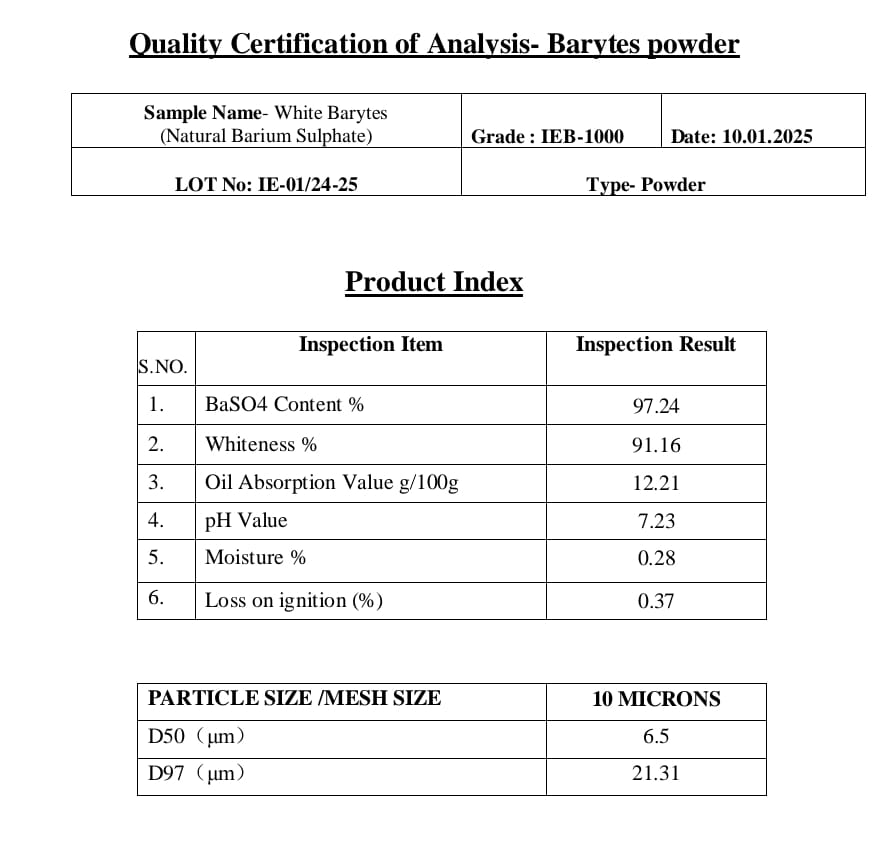
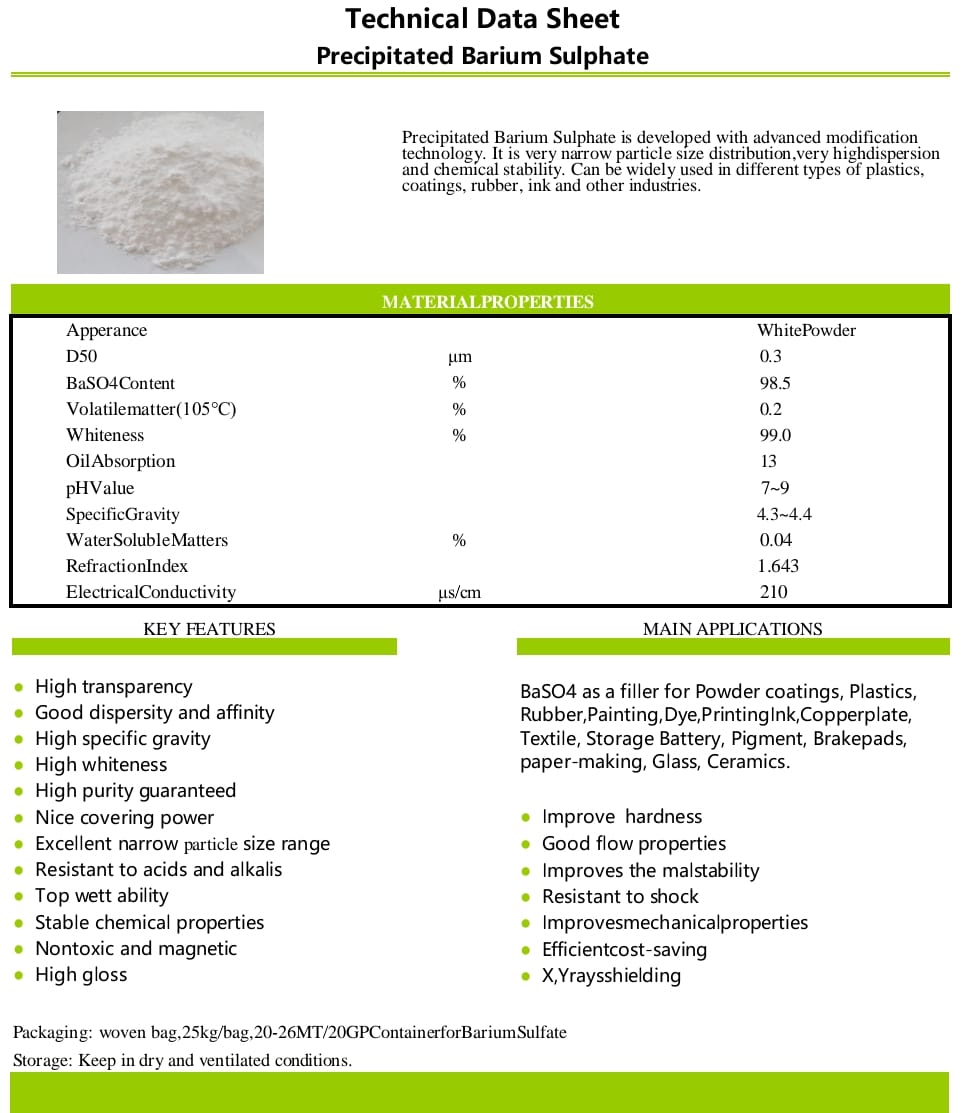
Mineral Name: Baryte, Barite powder (BaSO4)
Chemical properties:
| Moh’s hardness | Cleavage | Occurs in | Color | S.G. | Class | Chemical characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Three cleavages meet at 90°. | Especially in sedimentary rocks. | White | 4.5 | Sulfates | Alkaline earths or metals in combination with sulfate (SO42-) |
Barite is a mineral having barium sulfate (BaSO4). It obtained its name from the Greek word “barys” which means “heavy.” Baryte is a nonmetallic mineral with high specific gravity makes it suitable for a wide range of industrial, medical, and manufacturing uses. Barite also serves as the main ore of barium.
Barite deposits can be divided into the following four main types: bedded-sedimentary; bedded-volcanic; vein, cavity-fill, and metasomatic; and residual. Bedded sedimentary deposits, which are found in sedimentary rocks with characteristics of high biological productivity during sediment accumulation,
Most barite deposits have low impurity levels because (a) deposits typically form as precipitates from aqueous fluids, and (b) barium partitions more strongly into the sulfate mineral than strontium, lead, and other potential impurities. Calcium replacement of barium is also restricted in natural occurrences.
Bedded deposits are excavated by open-pit methods. The deposits are usually widespread with consistent barite grades.
Vein deposits are excavated by shafts, horizontal passage and by shallow open pits.
Beneficiation:
Improvement of physical and chemical properties of barite ore involves the following methods:
- Flotation.
- Heavy media.
- Magnetic separation.
In processing, initial crushing is carried out if there are impurities, such as waste rock or other minerals like fluorite, quartz, galena or pyrite. These may be separated from the barite by gravity separation, magnetic separation, and froth floatation. The barite is then either dried and sold as a powder, or processed further for particular applications.
Baryte uses:
Barite (barium sulfate, BaSO4 ) is an industrial mineral commodity that is used primarily in the drilling of oil and gas wells. The mineral commodity is also referred to as baryte or barite. It is a key constituent of drilling mud, which is the fluid pumped into the oil or gas well to lubricate the bit and drill stem, remove rock chips, prevent collapse of well walls, and prevent blowouts.
Other minor uses of the mineral include its use as an additive for friction materials, paints, plastics, rubbers, and other products; feedstock for chemical manufacturing.
Barium, which constitutes 59 percent of barite by weight, is used in ceramic glazes, enamels, optical glass, primers, signal flares, steel hardeners, welding fluxes, and a variety of other products.
Different grades of Baryte (Baryte)ium Carbonate available at Intercity Enterprises:
We offer a Wide variety of
- Barite/Barytes Off color/ half White
- Barite/Barytes Snow White
- Barite/Barytes Extra Super Snow White
- Grey Barytes
- Barite/Barytes Silica < 1%
- Barite/Barytes Silica < 3%
- Barite/Barytes Silica < 5%
Baryte uses in PVC:
Intercity enterprises is a manufacturer of barytes based in Chennai which is used in PVC to Improve performance:
Heat resistance: Barium sulfate, as an inorganic substance, has high heat resistance. Adding it to PVC can significantly improve the heat resistance of the product.
Abrasion resistance: Barium sulfate can enhance the wear resistance of PVC and extend the service life of the product.
Hardness and strength: Barium sulfate has high hardness. Adding it to PVC can increase the hardness and strength of the product and improve the mechanical properties of the product.
Improve appearance:
Glossiness: Barium sulfate, especially high-gloss barium sulfate, has excellent surface glossiness. Adding it to PVC can significantly improve the gloss effect of the product and improve the appearance quality of the product.
Chemical stability:
Chemical corrosion resistance: Barium sulfate has strong chemical inertness, good stability, acid and alkali corrosion resistance, and can protect PVC products from chemical corrosion.
Functionality improvement:
Absorb harmful rays: Barium sulfate can absorb harmful rays, such as X-rays, which is particularly important in medical and health equipment and other fields that require radiation protection.
Other functionality: Through modification, barium sulfate can also give PVC products other special functions, such as antistatic and heat preservation.
Processability optimization:
Molding processability: The addition of barium sulfate can improve the processing performance of PVC, such as improving the fluidity of the resin, which is beneficial to the molding and processing of the product.
Economic considerations:
In summary, the application of barium sulfate in PVC has many advantages, including improving product performance, improving appearance, enhancing chemical stability, improving functionality, optimizing processability and reducing costs. These advantages make barium sulfate an important filler choice in PVC products.