Mineral Name: Kaolin / China clay (Al2Si2O5(OH)4)
Chemical properties:
| Moh’s hardness | Occurs in | Color | S.G. | Class | Chemical Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Common clay mineral in soil and sedimentary rocks that includes montmorillonite. | white | 2.6 | Phyllosilicates | The composition of kaolinte is Al2O3, 39.8% SiO2 46% and H20 13.9%. |
The name “kaolin” is derivative of the word Kau-Ling, or high ridge, the name given to a mount near Jau-chau Fu, China, where kaolin was first mined.
Kaolin, usually referred to as china clay, is a clay that contains mainly of kaolinite (85%–95%).
Kaolinite is formed mainly by decomposition of feldspars (potassium feldspars), granite, and aluminium silicates.
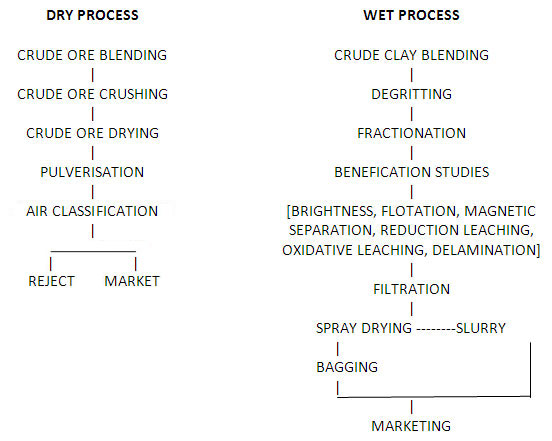
Kaolin is generally excavated from the mines in large moist lumps, and the primary process of refining involves mainly a change in the physical state. Two main methods have been used for the refining of the natural clay, which are the air flotation method or dry process method, and the wet process method. In the dry process, the clay is dried, pulverized, and then carried by currents of hot air into classifying chambers, from which it emerges as a stream of finely powdered kaolin.
Clay deposits are classified into two categories. The situ or residual deposits which are found near host rock are formed due to decomposition and disintegration of the feldspathic content present in the host rocks. These clays are coarsely grained with low plasticity. Whereas, the secondary category of transported deposits occur away from the source of formation. These clays are fine grained with high plasticity. The transported kaolin is pure as compared to situ deposits.
Beneficiation:
Natural kaolin clay contains wide varieties of impurities but Ph of clay also varies from deposit to deposit. The coarser impurities generally are quartz, mica, iron bearing minerals and heavy minerals. Fine impurities like TiO2, pyrite, organic matter, illite, montomorillonite, smectite, etc.. usually occur in very fine form in micron size along with fine kaolin clay.
The primary step in clay processing is to separate the abrasive minerals like quartz and undesirable minerals such as mica. The process is simpler in case of secondary deposits which have undergone natural classification during transportation, whereas the separation of kaolin from primary deposits is more difficult due to the presence of a high proportion of abrasive minerals that have survived the alteration process. The two methods are dry process and wet process.
Kaolin uses:
In ceramic industry china clay is an main constituent in manufacturing of porcelains. Like white-ware, electrical insulators and sanitary wares.
In paper industry used as filler and also for paper coating for stick paper. As filler in all grades of rubber goods like automobile tyres, pressed and moulded goods. It is used as an additive in cement industry. In paint, it is used as an inert extender, in white wash, emulsion paints and distemper paints. As a mild abrasive in polishes, tooth powder and cleaning soaps.
Different types of kaolin:
- Hydrous Kaolin
- Calcined Kaolin
- Crude Kaolin
Different grades of Kaolin (China clay) available at Intercity Enterprises:
- CRUDE (RAW) CLAY
- Pink China clay
- Seived clay
- White China clay – Grade 1
- White China clay – Grade 2


